Understanding Basal Cell Carcinomas and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) and Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) are two of the most common types of skin cancer, with millions of cases diagnosed each year. Understanding these cancers’ characteristics, risk factors, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. Here’s what you need to know:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
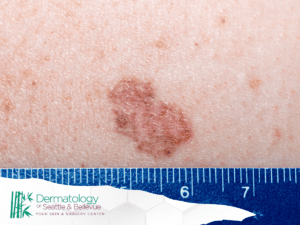
Basal Cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of all skin cancer diagnoses. These cancers typically develop in skin areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, head, and neck. BCCs often appear as raised, shiny bumps or growths that may bleed or develop a crust.
Risk Factors:
The primary risk factor for basal cell carcinomas is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Fair-skinned individuals with a history of sunburns or outdoor occupations are at higher risk of developing BCCs. Other risk factors include a family history of skin cancer, exposure to radiation therapy, and a weakened immune system.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for basal cell carcinomas typically involves surgical removal of the cancerous lesion. Depending on the size, location, and extent of the cancer, Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, cryotherapy, and topical medications such as imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil may be recommended.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 20% of diagnoses. It often develops in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, hands, and arms. These cancers may appear as red, scaly patches, open sores, or warts that may bleed or develop a crust.
Risk Factors:
Similar to BCCs, prolonged exposure to UV radiation is the primary risk factor for squamous cell carcinomas. Additional risk factors include a history of sunburns, outdoor occupations, older age, fair skin, a history of smoking, and a weakened immune system.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for squamous cell carcinomas may involve surgical removal of the cancerous lesion, Mohs micrographic surgery, radiation therapy, cryotherapy, laser therapy, or topical medications such as imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil. The choice of treatment depends on the cancer’s size, location, and aggressiveness.
Prevention:
Preventing basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas involves minimizing exposure to UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds.
This includes wearing sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding indoor tanning. Regular skin examinations and self-checks can help detect skin cancer early when it’s most treatable.
It is important to understand the causes, risks, and treatments for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. This knowledge can help prevent and effectively manage these types of skin cancer.
Understanding the causes can help in taking preventive measures. Knowing the risks can help in early detection and treatment. Being aware of the treatments available can help in managing the conditions effectively.

Maximizing Benefits: Advantages of Mohs Surgery for Skin Cancer
Mohs micrographic surgery, commonly known as Mohs surgery, is a specialized technique used to treat skin cancer with unmatched precision and effectiveness. This procedure offers several advantages over traditional methods, making it a preferred choice for many patients and dermatologists alike. Here are some of the key advantages of Mohs surgery for treating skin cancer:
- Highest Cure Rates:
Mohs surgery boasts the highest cure rates for both basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), the two most common types of skin cancer. Studies have shown cure rates as high as 99% for primary BCCs and 97% for SCCs, surpassing those of other treatment modalities.
This exceptional success rate is attributed to the meticulous removal of cancerous tissue layer by layer until no cancer cells remain, ensuring complete eradication of the tumor.
- Preservation of Healthy Tissue:
One of the hallmark features of Mohs surgery is its ability to spare as much healthy tissue as possible while removing cancerous cells. Mohs surgery precisely targets the tumor to minimize damage to nearby tissue. This differs from traditional surgeries, which typically remove a large margin of surrounding tissue.
This preservation of healthy tissue is particularly crucial for skin cancers located in cosmetically sensitive areas, such as the face, where maintaining optimal aesthetics is paramount.
- Precise Margin Assessment:
Mohs surgery allows for real-time microscopic examination of excised tissue, enabling the surgeon to accurately assess the margins. The surgeon can see how far the tumor has spread by examining each layer of tissue immediately. This helps ensure that all cancer cells are removed accurately.
This meticulous margin assessment minimizes the risk of leaving residual cancer behind, reducing the likelihood of recurrence and the need for additional surgeries.
- Cosmetic Excellence:
The precise nature of Mohs surgery lends itself to superior cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional excisional techniques. By selectively removing cancerous tissue while preserving healthy skin, Mohs surgery minimizes scarring and tissue distortion, resulting in optimal cosmetic results. This is particularly advantageous for skin cancers located on the face, where aesthetics play a significant role in patient satisfaction and quality of life.
- Minimally Invasive:
Mohs surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia, making it minimally invasive and well-tolerated by patients. Mohs surgery allows patients to go home on the same day and return to normal activities quickly. This is different from other surgeries that are more invasive. Mohs surgery is a popular choice for treating skin cancer because it is convenient and allows for quick recovery, leading to high patient satisfaction.
In short, Mohs surgery is a great choice for treating skin cancer. It has high cure rates and saves healthy tissue.
The procedure checks margins precisely and has good cosmetic results. Additionally, it is minimally invasive. These benefits make Mohs surgery an invaluable tool in the fight against skin cancer, providing patients with optimal outcomes and peace of mind.

Understanding Medicare Coverage for Mohs Surgery
When considering Mohs surgery, understanding Medicare coverage is crucial. Here’s what you need to know:
- Eligibility Criteria: Medicare typically covers Mohs surgery for the treatment of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. However, coverage may vary depending on individual circumstances and the specific Medicare plan.
- Medicare Part B Coverage: Mohs surgery is usually covered under Medicare Part B, which includes coverage for medically necessary outpatient services. This coverage extends to procedures performed in an outpatient setting, such as a dermatologist’s office or surgical center.
- Medically Necessary Criteria: To qualify for Medicare coverage, a healthcare provider must deem Mohs surgery medically necessary. This determination is based on factors such as the type and stage of skin cancer, as well as the location of the lesion.
- Cost Sharing: While Medicare covers a portion of the cost of Mohs surgery, beneficiaries are responsible for certain out-of-pocket expenses, including deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. These costs can vary depending on factors such as the specific Medicare plan and whether the provider accepts the assignment.
- Preauthorization Requirements: Some Medicare plans may require preauthorization or prior approval for Mohs surgery. This means that your healthcare provider must obtain approval from Medicare before the procedure can be performed. Failure to obtain preauthorization may result in coverage denial or higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Participating Providers: It’s essential to ensure that your dermatologist or surgeon participates in Medicare and accepts assignment. Providers who accept assignment agree to accept Medicare’s approved amount as full payment for covered services, which can help minimize your out-of-pocket costs.
- Coverage Limitations: While Medicare covers Mohs surgery for the treatment of skin cancer, certain limitations and exclusions may apply. For example, Medicare typically does not cover cosmetic procedures or treatments deemed experimental or investigational.
Knowing how Medicare covers Mohs surgery can help you make better choices about your healthcare and treatment. Talk to your doctor and Medicare rep to know what your insurance covers and any costs for Mohs surgery.
Does Dermatology of Seattle & Bellevue Work with Medicare?
Yes, Dermatology of Seattle & Bellevue works with Medicare for eligible patients. Contact us to learn more about our Medicare coverage options.