Moles are a common part of our skin landscape, but it’s natural to wonder: can a mole disappear on its own? While some moles do fade or vanish over time, others may signal changes that need medical attention. Understanding the nature of moles, their causes, and what to watch for helps you stay informed and proactive about your skin health.
Quick Summary
- Moles (nevi) are benign skin growths made of melanocyte clusters; they vary in size, shape, and color and are usually harmless.
- Moles form due to genetics and sun exposure, and can appear at birth or develop during childhood/adolescence; hormonal changes in puberty or pregnancy can trigger new moles or changes.
- Some benign moles can fade or disappear gradually over months or years, often with lightening, flattening, reduced size, or hair loss in the area.
- A disappearing mole can sometimes be linked to an immune response and may be associated with melanoma; seek prompt evaluation for rapid changes, irregular color/borders, bleeding, itching, pain, or dark centers.
- Treatment is typically unnecessary unless a mole changes or is a cosmetic concern; dermatologists may remove or biopsy suspicious moles, and prevention includes sun protection and monitoring for new or changing spots.
Definition of a Mole
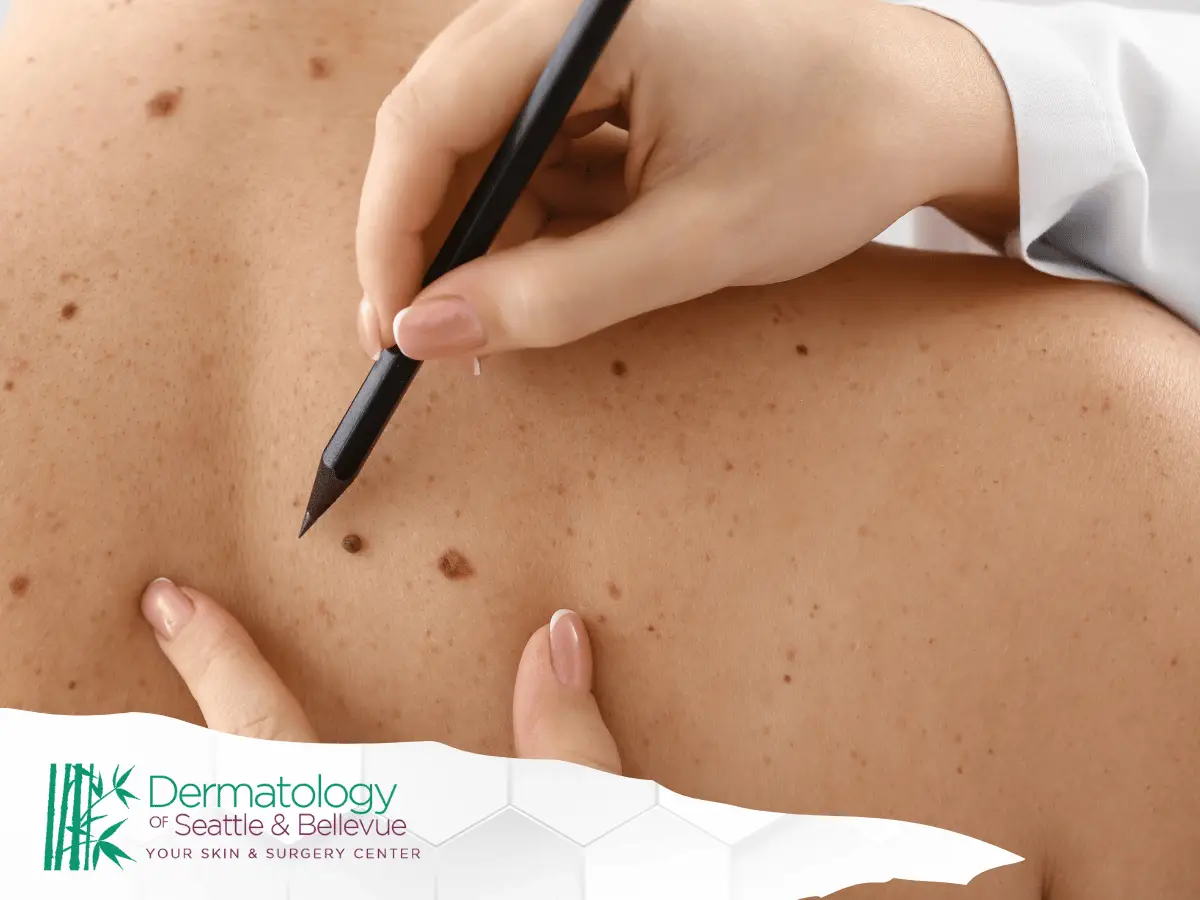
A mole, medically called a nevus (plural: nevi), is a benign growth on the skin formed by clusters of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. These small, usually brown or black spots can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size, shape, and color. Most moles are harmless, but some types require monitoring due to potential risks.
Causes of Moles
- Moles develop due to a combination of genetic factors and sun exposure that stimulates the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
- Some moles are congenital nevi, present at birth, while others appear during childhood or adolescence.
- Hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy can cause new moles to form or existing ones to change.
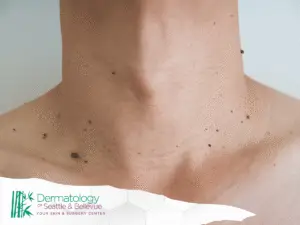
Types of Moles
Moles come in a wide range of appearances and types. The majority of moles are common, but certain types require closer attention:
- Common moles: Usually uniform in color and round or oval in shape.
- Atypical moles: Larger, with irregular borders and varied color. These have a higher risk of developing into melanoma.
- Congenital nevi: Present at birth and can vary in size. Large congenital nevi may carry a higher risk of skin cancer.
Signs of a Disappearing Mole
A mole that fades or disappears over time can be part of its typical life cycle, especially for benign moles. Signs of a disappearing mole include:
- Gradual lightening or loss of pigment
- Reduction in size or flattening
- Loss of hair in the mole area
- Changes occurring over months or years without other symptoms
Potential Risks of a Disappearing Mole
- While many disappearing moles are harmless, some could indicate an immune response targeting melanocytes, sometimes associated with melanoma.
- Watch for these warning signs that warrant immediate medical attention:
- Rapid changes in color or size
- Irregular or uneven color patches
- Bleeding, itching, or pain
- Irregular shapes or poorly defined border or edges
- Presence of black dots or dark centers
- Early evaluation by a dermatologist is essential to rule out malignant melanoma or other skin cancers.
Treatment Options for Moles
Most moles don’t require treatment unless they show signs of change or cause cosmetic concerns. When necessary, treatments include surgical removal through excision or shaving, often done as a harmless procedure by a dermatologist. Biopsies may be performed to analyze suspicious moles under a microscope to rule out skin cancer.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you notice any changes in your moles or if a mole begins to disappear unexpectedly, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Early consultation ensures timely diagnosis and intervention, especially if signs of melanoma or other cancers are present. Regular check-ups and monitoring by a dermatologist help maintain optimal skin health. In addition to being vigilant about changes in your moles, it is advisable to follow mole examination recommendations from your dermatologist to identify any potential issues early. These recommendations often include regular self-examinations and professional check-ups, which can significantly reduce the risk of serious skin conditions. Staying informed about your skin’s health is key to prevention and successful treatment.
Prevention Tips for Moles
- Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and use broad-spectrum sunscreen regularly.
- Avoid intentional tanning and protect your skin with clothing and hats.
- Monitor the number of moles and report any new or changing spots to your healthcare provider.
- Maintain a healthy diet and skincare routine to support overall skin health.